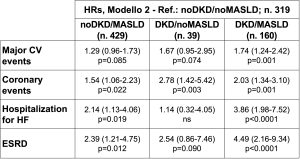
Background: MASLD and DKD often coexist in T2DM; both are associated with a high risk of CV events and death. The combined effects of DKD and MASLD (“formerly” NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) on CVD incidence and all-cause mortality were evaluated in 961 T2DM. Materials and methods: Death and incidence of CVD (947 subjects), were censored on December 31st, 2017. DKD was defined as eGFR<60 ml/min/1.73 m2 and/or UACR ≥30 mg/g. MASLD was defined as Fatty Liver Index ≥60 (based on triglycerides, gamma-GT, BMI, waist circumference). HRs and 95% CIs for outcomes related to DKD, MASLD, or both were assessed in adjusted Cox regressions. Results – 325 subjects (33.8%) were noDKD/noMASLD, 435 (45.2%) noDKD/MASLD, 39 (4.1%) DKD/noMASLD and 162 (16.9%) DKD/MASLD. Both MASLD+ subgroups showed metabolic unfavorable profile and worse inflammatory profile, while both DKD+ subgroups had higher blood pressure and rate of hypertension. Estimated glucose disposal rate (eGDR, a proxy of insulin resistance) was higher in all subgroups compared with noDKD/noNAFLD. There were 229 deaths (23.8%), 273 major CVD (28.8%), 181 coronary events (CHD: 19.1%), 82 hospitalization for heart failure (hHF, 8.7%), 101 cerebrovascular events (10.7%), 39 peripheral vascular events (4.1%) and 71 ESRD (7.5%). In the DKD-MASLD subgroups, deaths were 16.3, 21.8, 25.6 and 43.8% (p<0.0001) with adjusted HRs of 1.44 (1.03-2.02, p=0.034) for noDKD/MASLD, 1.05 (0.53-2.07) for DKD/noMASLD and 2.66 (1.85-3.82, p<0.0001) for DKD/MASLD. The table shows the effects of DKD-MASLD combinations on major CVD (p=0.010), CHD (p=0.002), hHF (p=0.001) and ESRD (p=0.001) towards noDKD/noMASLD. No independent association was observed with the incidence of cerebrovascular or peripheral vascular events. Conclusions: The coexistence of DKD and MASLD increases mortality and incidence of CV events in type 2 diabetes. MASLD alone is also associated with adverse outcomes. Monitoring and management of DKD and MASLD are necessary to prevent CV events and reduce mortality in type 2 diabetes. Funding: PRIN 2020 (2020SH2ZZA).