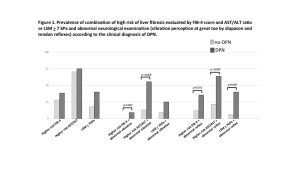
Background: Hepatic steatosis and diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) share etiological and clinical correlates, while relationship between liver fibrosis and DPN has not been well investigated. AIMS. To evaluate the association between liver fibrosis and DPN and investigate the non-invasive scores of fibrosis as predictors of DPN. Methods: Observational, cross-sectional study including individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and steatosis. Neurological assessment was performed with Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument-Q (MNSI-Q), Michigan Diabetic Neuropathy Score (MDNS) and Diabetic Neuropathy Index (DNI). Fibrosis risk was estimated using Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4), NAFLD Fibrosis Score (NFS), AST/ALT ratio, and AST to platelet ratio index (APRI). Finally, fibrosis was defined by liver stiffness measurement (LSM) ≥7.0 kiloPascals (kPa) at Fibroscan. Results: Eighty-six T2D subjects (mean age 59.22±13.18 years, diabetes duration 9.61±8.87 years, HbA1c 57.71±14.28 mmol/mol, 69.8% males) were included. DPN was detected in 43% of the cohort. Higher FIB-4 and AST/ALT scores were detected in subjects with DPN compared to those without DPN (FIB-4 1.23±0.66 vs 1.63±0.85, p 0.018; AST/ALT 0.89±0.23 vs 1.11±0.61, p 0.026). Moreover, the DPN group showed higher LSM (6.56±4.23 kPa vs 7.12±3.58 kPa, p 0.619) and the MDNS score was correlated with LSM (Rho 0.304, p 0.026). At neurological examination, a higher prevalence of alteration was observed in vibration by diapason or reflexes in subjects with fibrosis compared to LSM<7 kPa (p 0.025 and p 0.042, respectively). Finally, a qualitative evaluation of vibration or reflexes in individuals with high FIB-4 and/or AST/ALT indexes was associated with DPN (FIB-4+vibration: p 0.047; FIB-4+reflex: p 0.013; AST/ALT+vibration: p<0.001; AST/ALT+reflex: p<0.001). Conclusions: Exploring easy-to-apply screening methods, the qualitative evaluation of vibration or reflexes would appear effective in identifying DPN in T2D with steatosis.